Ligase Dna Replication | These include vaccinia virus, african swine fever virus, and chlorella virus pbcv1. The majority of ligation reactions involve dna fragments that have been generated by restriction enzyme digestion. Watson and crick immediately saw the relationship of the double helix to genetic replication. Chimeric proteins with dna ligase i and the green fluorescent protein localized at replication foci in living mammalian cells and thus show that these subnuclear functional domains, previously observed in fixed cells, exist in vivo. It has important role in the process of dna replication and dna repair.
It seals repairs in the. These include vaccinia virus, african swine fever virus, and chlorella virus pbcv1. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. Dna ligase transfers an amp residue to the 5′ phosphate end of one of the dna fragments to be bound. Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound.
During dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new once replication is completed, the rna primers are replaced by dna nucleotides and the dna is sealed with dna ligase. Dna replication is fundamental process occurring in all living organism to copy their dna. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. Dna ligase iii and dna ligase iv carry out genetically distinct forms of end joining in human somatic cells. negative regulation of mitochondrial dna replication source: Watson and crick immediately saw the relationship of the double helix to genetic replication. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. Our previous finding that lig1 knockout mouse embryos developed normally to. Dna replication is the process by which an organism duplicates its dna into another copy. This is the currently selected item. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the. Dna ligase transfers an amp residue to the 5′ phosphate end of one of the dna fragments to be bound. It seals repairs in the. The majority of ligation reactions involve dna fragments that have been generated by restriction enzyme digestion.
This is the currently selected item. Dna replication occurs when the dna strands unzip, and the original strands of dna serve as a template for new nucleotides to another enzyme, dna ligase , is then able to attach (ligate) the dna nucleotides together, completing the synthesis. Dna replication is the process by which an organism duplicates its dna into another copy. Dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together.
These include vaccinia virus, african swine fever virus, and chlorella virus pbcv1. Dna replication is fundamental process occurring in all living organism to copy their dna. Eukaryotic dna replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts dna replication to once per cell cycle. This video explains the mechanism of dna ligase. Dna ligase iii and dna ligase iv carry out genetically distinct forms of end joining in human somatic cells. negative regulation of mitochondrial dna replication source: Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound. The current article provides a short insight into the complex dna replication steps. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Our previous finding that lig1 knockout mouse embryos developed normally to. Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components: Watson and crick immediately saw the relationship of the double helix to genetic replication. Eukaryotic dna replication of chromosomal dna is central for the duplication of a cell and is necessary for the maintenance of. It has three general functions:
Dna replication is the process by which an organism duplicates its dna into another copy. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. It has three general functions: Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. Eukaryotic dna replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts dna replication to once per cell cycle.
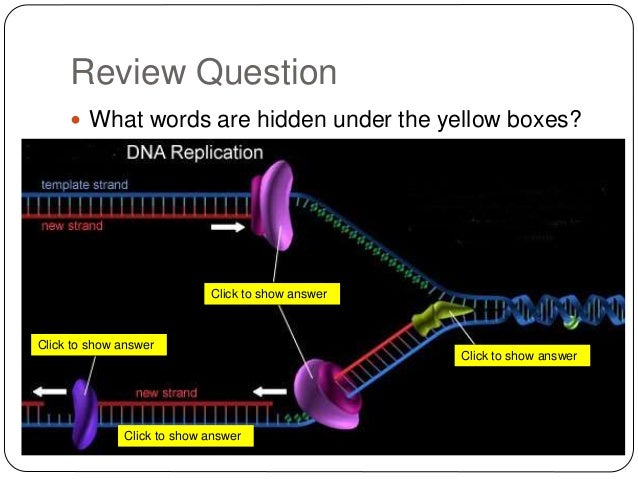
This is the currently selected item. Aberrant dna repair and dna replication due to an inherited enzymatic defect in human dna ligase i. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. Dna replication occurs when the dna strands unzip, and the original strands of dna serve as a template for new nucleotides to another enzyme, dna ligase , is then able to attach (ligate) the dna nucleotides together, completing the synthesis. Dna replication is carried out by a complex system of enzymes. Watson and crick immediately saw the relationship of the double helix to genetic replication. .of flashcards about term:enzymes dna replication = dna ligase on quizlet. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. The current article provides a short insight into the complex dna replication steps. Dna replication — steps & diagram. However, the dna repair protein xlf, which interacts with. Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components:
The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together ligase dna. Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound.
Ligase Dna Replication: Aberrant dna repair and dna replication due to an inherited enzymatic defect in human dna ligase i.
comment 0 comments
more_vert